microic.github.io
LogReLU
LogReLU can be simply defined as log(max(x, 0) + 1). Following is a PyTorch implementation of LogReLU:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def log_relu(x):
return torch.log(F.relu(x) + 1)
x = torch.linspace(-2, 4, 10000)
y1 = F.relu(x).numpy()
y2 = log_relu(x).numpy()
x = x.numpy()
fig1, = plt.plot(x, y1)
fig2, = plt.plot(x, y2)
plt.legend(handles=[fig1, fig2], labels=['ReLU', 'LogReLU'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
LogReLU vs ReLU:
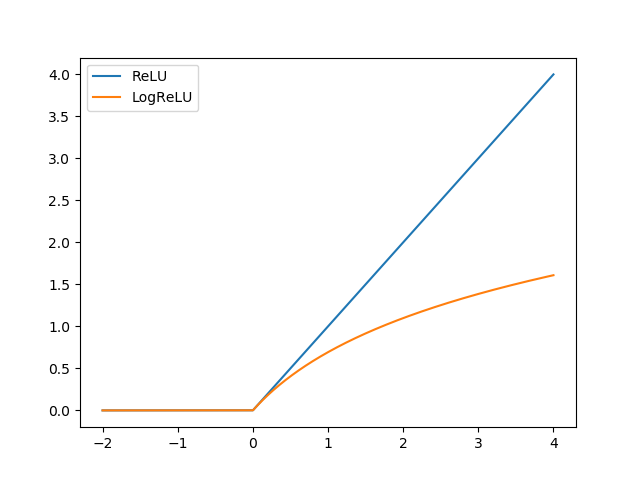
As you can see, LogReLU can avoid the output from being too large
It is also very easy to get the gradient of LogReLU:
g = 1 / (x + 1) if x > 0 else 0
When to use LogReLU?
- If you get NaN/Inf error when training deep learning networks
- If you want to avoid the output from being too large
Links
http://xuebao.jlu.edu.cn/lxb/EN/Y2017/V55/I03/617